According to Michael Porter’s 1979 theory, any industry’s competition is driven by five competitive forces: Bargaining power of buyers Nature and intensity of the rivalry amongst competitors Threat of new entrants Threat of substitute products or services The bargaining power of suppliers The composition and strength of these forces collectively determine the nature of industry competition and the average profitability for incumbent competitors. Industry structure changes when new technology, customer needs, or other factors shift these five forces. Smart, connected products, or the Internet of Things (IoT), will substantially affect structure in many industries, not least smart commercial buildings and home automation, as did the previous waves of IT in the 70s and internet-enabled IT in the 90s. Smart, connected products dramatically expand opportunities for product differentiation, moving competition away from price alone. Knowing how customers actually use the products enhances a company’s ability to segment customers, customise products, set prices to better capture value, […]
Most Popular Articles

MRI Software: Exploring the 2025 IPO & Sale Options
This Research Note examines a report from Reuters that MRI Software is to be listed in an IPO or sold. We explore the development of the business over the last 10 years, since it was acquired by private equity owners, highlight their software acquisitions for commercial real estate applications addressing integrated workplace management, tenant experience […]

Podcast 40: Stiles Property Management Found $400K+ in Hidden Savings
Most property managers know their buildings are hemorrhaging money through inefficient systems. The problem? They have no idea where to start looking. Devon Newton, VP of Property Management at Stiles, faced this exact challenge with 110 East, a new Class A development in Charlotte’s Southpark district. Despite managing 116 properties across the Southeast, she found […]
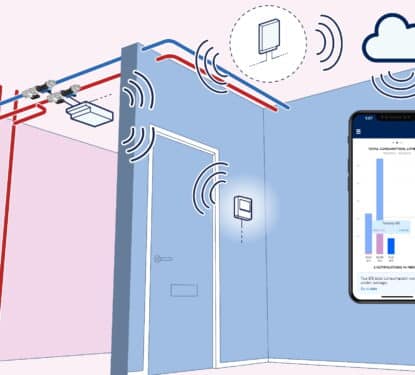
Smartvatten Strengthens European Position with 2025 LeakLook Acquisition
This Research Note examines Smartvatten, a Finnish specialist in water efficiency technology and expertise in Northern Europe. It updates our previous article in March 2024, covering Smartvatten’s solutions, key developments in 2024, sustainability partnerships and the September 2025 acquisition of LeakLook, a Finnish specialist in IoT-driven water monitoring for real estate. Smartvatten Profile Established in […]
