This article was written by Daphne Tomlinson, Independent Senior Research Associate at Memoori.
What Makes a Building Smart? This has been an ongoing debate in many articles and conference presentations over the years, as it means so many different things to different people; And it is not easy to articulate one universal definition which encompasses all building types, vertical markets and occupant needs.
There have been various digital controls in place in many buildings since around 1979. Those buildings have always been smart in some sense. The fact is that smart buildings have evolved over the years, as buildings have been digitized, closed environments have given way to open systems and the IoT has enabled building managers to collect data and conduct real-time analysis to improve how buildings operate.
While smart buildings have been traditionally associated with technology such as building automation or IoT, the focus is now shifting from technology to user experience. Putting the user experience at the centre of the design process and using technology as a “means to an end, not the end itself” will enable the industry to deliver buildings that are fit for purpose. The IoT is central to this process, as increasingly, buildings will be driven by data. Using the data available through IoT allows more informed decision-making related to facility operations and the use of the building by its occupants.
Our recent joint White Paper with Locatee, entitled “Navigating the Complex Smart Building Landscape”, is intended to help Corporate Real Estate and Facilities Management professionals address their priorities and navigate their path through the respective use cases towards a strategy for “smartening” their building portfolios. The white paper identifies 49 use cases which illustrate a diverse set of applications which can be found in Smart Buildings. You can download a Free Copy Here.
While the definition of a Smart Building will vary across building types and vertical markets, we believe that there are seven fundamental attributes or capabilities enabled by digitization, which can define a Smart Building.
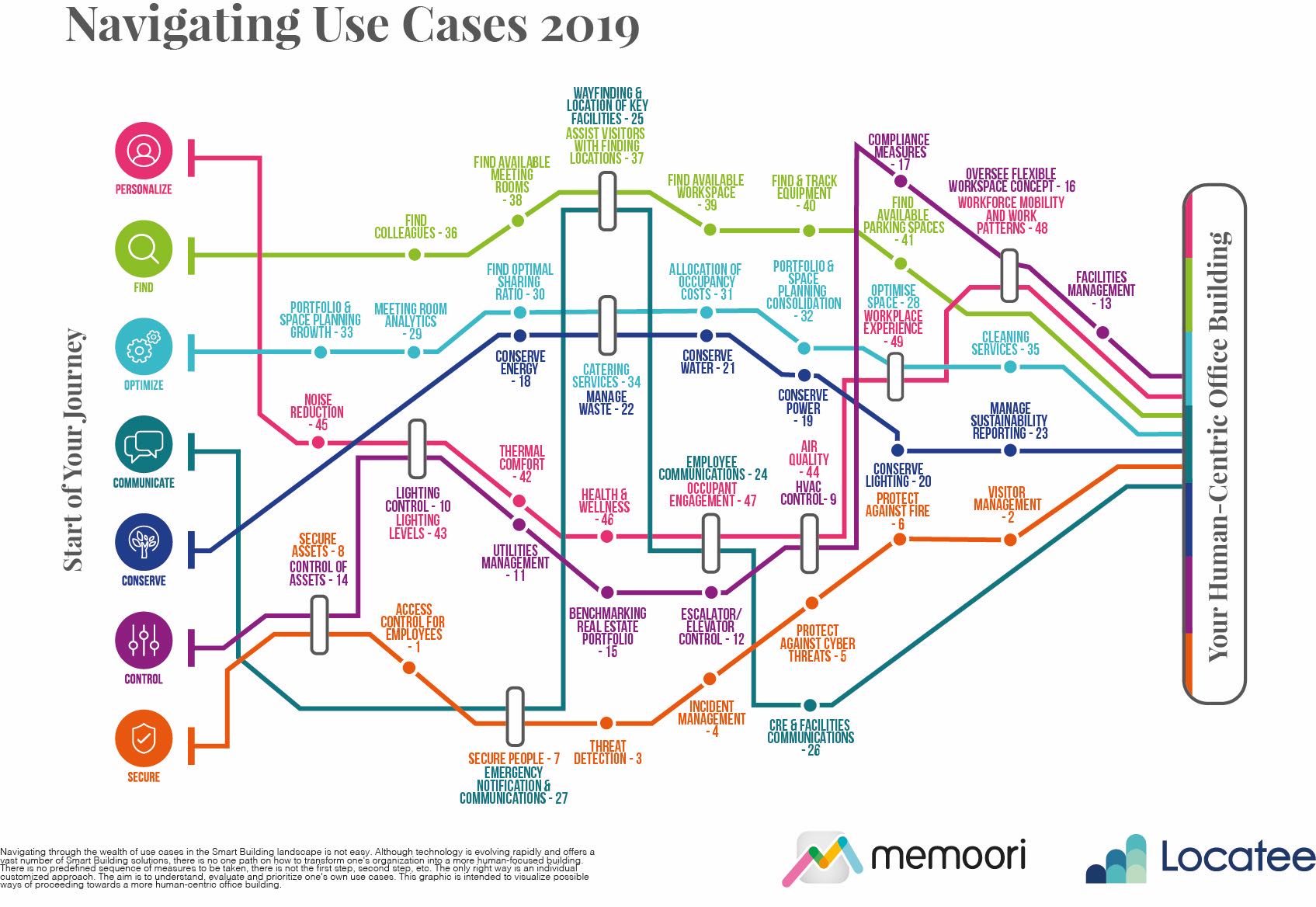
Each of these attributes provides the basis for a set of use cases, which can deliver tangible benefits. These attributes can also provide a framework for creating a smart building strategy, aligned to the overall business objectives of Corporate Real Estate owners and operators.
The focus of the Control and Conserve attributes is on use cases revolving around energy management, resource utilization, asset management and the benchmarking of real estate portfolios. The outcomes of these use cases can include improved energy efficiency, operational cost reduction and conservation and sustainability of resources.
The renewed emphasis on user-centric buildings has meant we are reaching a tipping point in the evolution of the workplace. Building owners and operators are becoming far more interested in increasing occupant well-being and productivity, as a means to attract talent and retain their most valuable asset, their people!
The focus of the Find, Optimize, Personalize and Communicate attributes is on satisfying the employees’ needs for human-centric buildings, providing an improved user experience and a healthy indoor environment for building occupants.
Securing people and assets is a fundamental attribute of Smart Buildings, which cannot be ignored. People are the most important assets within commercial organizations. In the event that threats become serious emergencies, such as fire or active shooter scenarios, it becomes essential to know where everybody is within the building so they can be evacuated and accounted for.
Smart buildings will continue to evolve as new ways of working become prevalent and priorities change. For most organizations, creating, adapting and implementing smart buildings with a variety of use cases will be a continuous incremental process of improvement rather than a one-off initiative.
Sign Up for our Free Webinar on Monday 24th June at 1700 CEST to discover more about our White Paper.